
Keep Your Pond Thriving: Smart Climate Solutions That Actually Work
Transform your pond’s resilience against extreme weather by implementing multi-layered adaptation strategies that protect both aquatic life and water quality. Understanding the climate impact on pond ecosystems enables targeted solutions for long-term sustainability.
Install adjustable depth zones and overflow systems to manage water levels during both drought and heavy rainfall events. Create natural buffer zones with native vegetation to reduce erosion, filter runoff, and provide shade during heat waves. Integrate automated monitoring systems to track water temperature, oxygen levels, and pH fluctuations, allowing rapid response to changing conditions.
These practical adaptations work together to build a robust defense against climate variability while maintaining your pond’s natural beauty and ecological function. Combined with smart water management practices and strategic plant selection, these measures ensure your pond thrives despite environmental challenges. Regular assessment and adjustment of these strategies keeps your water feature resilient and adaptable to evolving climate patterns.
Understanding Climate Threats to Your Pond
Temperature Changes and Water Quality
As our climate warms, pond water faces new challenges that can affect the entire ecosystem. Rising temperatures reduce the water’s ability to hold oxygen, which can stress fish and other aquatic life. Warmer water also speeds up algae growth and can throw off the delicate balance of beneficial bacteria in your pond.
The good news is that there are several ways to combat these effects. Natural pond aeration becomes even more crucial during warmer periods, helping to maintain healthy oxygen levels throughout your water feature. Adding floating plants can provide shade and help keep water temperatures more stable.
Keep an eye on your water’s pH levels during hot spells, as warming water can cause these levels to fluctuate more dramatically. Consider testing your water more frequently during summer months and after unusual weather events. Adding beneficial bacteria supplements can help maintain water quality when temperatures rise, ensuring your pond remains a thriving habitat despite climate challenges.
Extreme Weather Events
Extreme weather events can significantly impact your pond’s health and stability. During drought periods, decreased rainfall leads to lower water levels, which can stress fish and plants while concentrating potentially harmful substances in the remaining water. Installing a water level monitor and having a backup water source ready can help you maintain optimal levels during dry spells.
Heavy rainfall presents its own challenges, potentially overwhelming your pond with excess water and introducing unwanted debris, chemicals, or nutrients from runoff. Creating proper drainage systems and installing overflow pipes can help manage sudden water influxes. Consider adding rain gardens or bioswales around your pond to filter incoming water naturally.
Strong storms can damage pond equipment, uproot plants, and disturb fish populations. Secure all pond equipment firmly, and consider installing windbreaks using strategic plantings or structures. Having an emergency action plan is crucial – know how to protect your pond during severe weather alerts, including having backup power for essential equipment and temporary covers for vulnerable areas.
Remember to regularly inspect your pond’s infrastructure and maintain emergency supplies, especially before seasonal weather changes. This proactive approach helps ensure your pond remains resilient through various weather challenges.
Smart Design Solutions for Climate Resilience
Depth Zones and Temperature Control
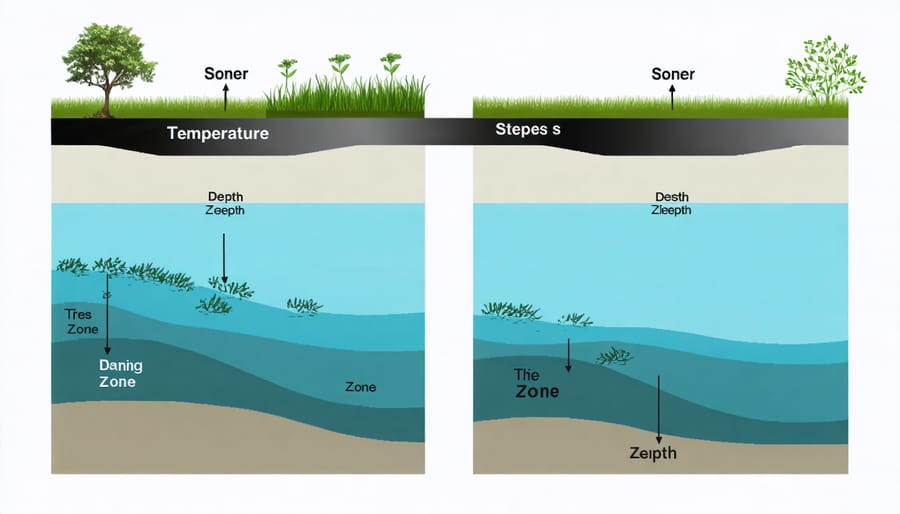
Creating different depth zones in your pond isn’t just about aesthetics – it’s a smart strategy for managing temperature fluctuations in changing climate conditions. Think of your pond as a layered cake, where each level serves a specific purpose in maintaining a stable environment.
The deep zone, ideally 4-6 feet deep, acts as a thermal refuge during extreme weather. When summer temperatures soar, fish and other aquatic life can retreat to this cooler bottom layer. In winter, this same depth prevents complete freezing, protecting your pond’s inhabitants.
Mid-depth zones, ranging from 2-4 feet, create a transitional area where water temperatures remain moderate. This zone is perfect for many aquatic plants and provides excellent coverage for fish moving between depths. It also helps regulate the overall pond temperature by creating a buffer between surface and bottom waters.
The shallow margins, typically 6-12 inches deep, serve multiple purposes. They’re excellent for marginal plants, which help shade the water and reduce temperature spikes. These areas also create essential microhabitats for beneficial insects and amphibians.
To maximize temperature control:
– Position deeper areas away from direct afternoon sun
– Include shelves or ledges at various depths
– Install plants strategically to provide shade
– Consider adding a small waterfall or fountain to increase oxygen levels and promote water movement
Remember to monitor water temperatures at different depths throughout the seasons. This helps you understand how your pond responds to weather changes and allows you to make adjustments as needed. During extreme weather events, these varied depth zones become crucial survival zones for your pond’s ecosystem.
Shade Management Strategies
Creating effective shade in your pond environment is crucial for adapting to increasingly warm temperatures. Natural shading methods, like strategically placed trees and shrubs, not only provide cooling benefits but also add visual appeal to your water garden. Consider planting deciduous trees on the southern or western sides of your pond, which offer shade during hot summers while allowing beneficial sunlight through during winter months.
Floating aquatic plants serve a dual purpose by providing shade and natural filtration. Water lilies, lotus, and floating heart plants can cover 40-60% of your pond’s surface, helping maintain cooler water temperatures while creating beautiful displays. For smaller ponds, miniature floating plants like duckweed or water lettuce work wonderfully.
When natural options aren’t feasible, artificial shade solutions can be equally effective. Shade sails, pergolas, and retractable awnings offer flexible coverage that you can adjust as needed. These structures can be particularly useful during extreme heat waves or when young plants are still establishing themselves.
For a more temporary solution, consider using shade cloth or mesh screens. These affordable options can be easily installed and removed as seasons change. When selecting artificial shade materials, opt for those that allow some light penetration (30-50% shade rating) to maintain a healthy balance for your pond ecosystem.
Remember to monitor your pond’s temperature and adjust shade coverage accordingly. Too much shade can limit plant growth and reduce beneficial algae, while too little may cause water temperatures to rise to dangerous levels for fish and other aquatic life.
Plant Selection for Climate Adaptability
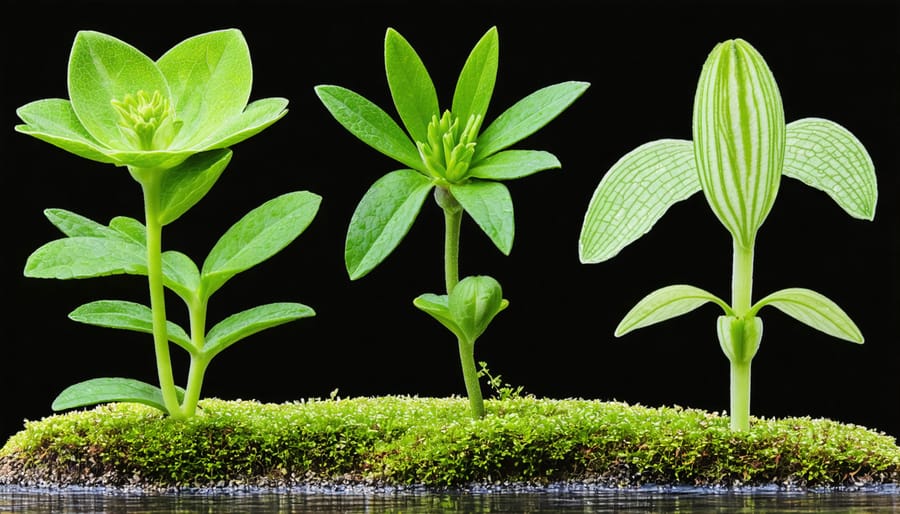

Hardy Native Species
When adapting your pond to climate changes, choosing the right native plants is crucial. These hardy species have evolved to handle local weather patterns and can better withstand temperature fluctuations. Among the most resilient options are essential emergent plants like rushes and sedges, which naturally protect pond edges while adapting to varying water levels.
Look for deep-rooted natives like water iris and pickerelweed, which help stabilize soil during extreme weather events. These plants also provide crucial shade that keeps pond temperatures stable during heat waves. Native water lilies are particularly valuable, as they spread their leaves across the surface, reducing water evaporation while creating wildlife habitats.
Consider including drought-resistant species like marsh marigold and swamp milkweed around your pond’s margins. These plants can handle both wet and dry conditions, making them perfect for unpredictable weather patterns. They’ll continue thriving even when water levels fluctuate, helping maintain your pond’s ecosystem balance.
For best results, plant in groups and layers, mixing different native species that bloom at various times. This approach ensures year-round coverage and creates a more resilient system that can bounce back from extreme weather events. Remember to choose plants native to your specific region, as these will be naturally equipped to handle local climate challenges.
Strategic Planting Zones
Creating strategic planting zones around your pond is one of the most effective ways to protect it from climate challenges. Think of these zones as natural shields that work together to maintain your pond’s health and stability.
Start by establishing a windbreak zone using taller plants and shrubs on the prevailing wind side of your pond. This helps reduce water evaporation and protects against harsh weather conditions. Consider hardy options like native grasses, viburnums, or small trees that can withstand local climate variations.
Next, create a buffer zone around the pond’s edge using moisture-loving plants. This zone acts as a natural filter, helping to manage water quality and reduce erosion during heavy rains. Mix different heights of plants, from ground covers to medium-height perennials, to create a layered effect that maximizes protection.
Don’t forget to include shade-creating plants on the south or southwest side of your pond. These help regulate water temperature during hot spells and reduce algae growth. Large-leafed plants like hostas or ferns work well in these areas.
For the best results, choose native plants adapted to your local climate. They’re naturally resilient and require less maintenance. Remember to space plants appropriately, allowing room for growth while maintaining good air circulation. This strategic approach to planting not only protects your pond but also creates a beautiful, natural-looking landscape that enhances your outdoor space.
Water Management Techniques
Water Conservation Methods
Water conservation is crucial for maintaining healthy pond ecosystems during climate challenges. Start by installing a water level monitor to track fluctuations and identify potential leaks early. Consider adding a pond liner if you haven’t already – this simple addition can significantly reduce water loss through ground seepage.
Incorporate natural water-saving techniques like adding a layer of floating plants to reduce evaporation. Water lilies and duckweed are excellent choices, as they provide shade and help maintain cooler water temperatures. Install a rainfall collection system to capture and store rainwater for topping up your pond during dry spells.
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in water conservation. Check your pump system for leaks and ensure all pipe connections are secure. Consider installing a timer on your fountain or waterfall features, running them during cooler hours to minimize water loss through evaporation.
Create a buffer zone around your pond using moisture-retaining plants and mulch. This helps slow water runoff and maintains soil moisture levels. During extreme heat, consider using pond netting or shade sails to reduce evaporation rates.
For larger ponds, implement a water recycling system that captures and filters runoff water. This not only conserves water but also helps maintain water quality. Remember to regularly monitor water quality parameters, as concentrated minerals from evaporation can affect pond health.
Consider upgrading to energy-efficient pumps and filtration systems that use less water for backwashing. These modern systems often come with smart controls that help optimize water usage while maintaining proper circulation.
Water Quality Maintenance
As climate patterns shift, maintaining stable water quality becomes increasingly challenging yet crucial for pond health. Regular water quality testing helps you stay ahead of potential issues and adapt your maintenance routine accordingly.
Start by monitoring temperature fluctuations, as warmer water holds less oxygen and can stress pond life. Installing an aerator or fountain can help maintain healthy oxygen levels during heat waves. Keep an eye on pH levels too, as increased rainfall or drought can cause unexpected swings that affect fish and plant health.
Consider installing a UV clarifier to combat increased algae growth, which often results from warmer temperatures and longer sunlight exposure. Adding beneficial bacteria monthly helps break down excess nutrients and maintain a balanced ecosystem, especially important when weather patterns are unpredictable.
Create a seasonal maintenance calendar that accounts for local climate trends. During extended dry periods, top up water levels gradually to avoid shocking the system. After heavy rains, check for sudden changes in water chemistry and adjust treatments accordingly.
Remember to maintain your filtration system more frequently during extreme weather events, as debris and organic matter tend to accumulate faster. A well-maintained filter helps your pond adapt to changing conditions while keeping the water crystal clear and healthy for all inhabitants.
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, adapting our ponds to climate change isn’t just about responding to current challenges – it’s about preparing for the future. By implementing these adaptation strategies, you’re taking proactive steps to protect your pond ecosystem and ensure its long-term health and beauty.
Remember that successful climate adaptation starts with careful observation of your pond’s specific needs. Whether it’s installing shade structures, selecting climate-resilient plants, or implementing smart water management systems, each strategy plays a vital role in creating a more resilient water feature.
Don’t wait for problems to arise before taking action. Regular monitoring of water levels, temperature, and plant health will help you spot potential issues early. Start with small changes, like adding floating plants for shade or installing a basic water conservation system, and gradually build up to more comprehensive adaptations as needed.
Most importantly, stay flexible in your approach. Climate patterns can be unpredictable, and what works today might need adjustment tomorrow. Keep learning, stay connected with other pond enthusiasts, and be ready to modify your strategies as conditions change.
By taking these steps now, you’re not just protecting your investment – you’re creating a sustainable aquatic environment that can thrive despite climate challenges. Your pond can continue to be a source of joy and natural beauty for years to come.
