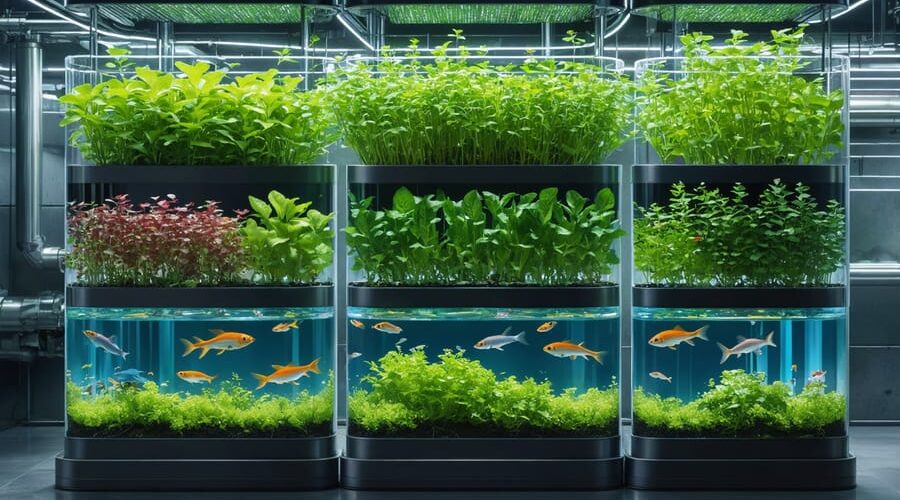

Space-Saving Vertical Aquaponics: Build Your Own Thriving Garden and Fish System
Transform your limited growing space into a sustainable food production powerhouse with a vertical aquaponic system, where fish and plants work together in perfect harmony. This innovative DIY aquaponics setup maximizes production by growing upward instead of outward, making it ideal for urban environments, small backyards, or indoor spaces.
Modern vertical aquaponics combines centuries-old farming wisdom with cutting-edge technology, creating a closed-loop ecosystem that uses 90% less water than traditional gardening while producing both fresh vegetables and protein-rich fish. By stacking growing beds vertically and utilizing efficient water circulation systems, these setups can yield up to four times more produce per square foot compared to conventional gardening methods.
Whether you’re a sustainability enthusiast, urban farmer, or space-conscious gardener, vertical aquaponics offers a practical solution for year-round food production. The system’s modular design allows for easy customization, making it possible to start small and expand as your experience grows. With proper planning and maintenance, a vertical aquaponic system can provide fresh herbs, leafy greens, and fish for your table while serving as a stunning, living demonstration of ecological principles in action.
Understanding Vertical Aquaponic Systems
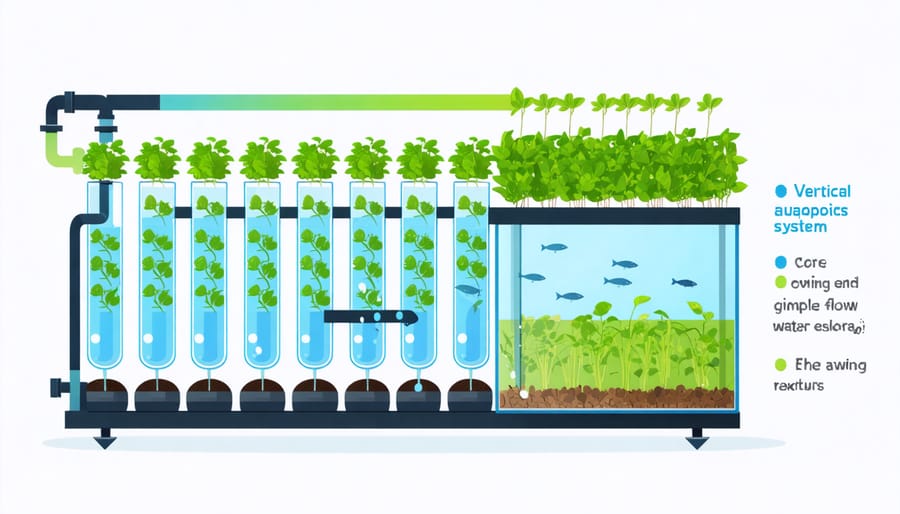
Core Components
A vertical aquaponic system relies on several essential system components working together harmoniously. At the base, you’ll find the fish tank, which houses your aquatic friends and serves as the nutrient source for your plants. These tanks should be sized appropriately for your chosen fish species, typically holding between 50-200 gallons of water.
Growing towers are the vertical elements where your plants thrive. These can be PVC pipes with holes cut for plant pods, or specially designed tower systems with multiple planting spots. The vertical design maximizes growing space while minimizing your system’s footprint.
The pumping system is the heart of your setup, circulating water from the fish tank up through the growing towers. You’ll need a reliable water pump sized to match your system’s height and volume. For most home systems, a 400-1000 GPH pump works well.
Filtration is crucial for maintaining water quality. A mechanical filter removes solid waste, while a bio-filter provides surface area for beneficial bacteria to convert fish waste into plant nutrients. Some systems include additional components like settling tanks or mineralization tanks to break down solid waste more efficiently.
Don’t forget about aeration – air stones in the fish tank and periodic water splashing in the towers ensure adequate oxygen for both fish and plant roots.
Space and Layout Requirements
When planning your vertical aquaponic system, start with a minimum space of 4 square feet for a basic setup. The ideal height ranges from 6 to 8 feet, allowing for multiple growing levels while keeping plants accessible for maintenance. Remember to leave at least 2 feet of walkway space around your system for easy access.
For optimal space efficiency, arrange growing towers in a north-south orientation to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day. Space towers approximately 18-24 inches apart to prevent overcrowding and ensure good air circulation. Each tower typically needs about 1 square foot of floor space, plus additional room for the fish tank below.
Your fish tank should occupy roughly 25% of your total system footprint. For a home-scale system, a 50-gallon tank works well and requires about 4 square feet of space. Position the tank at the lowest point of your system to allow gravity to assist water flow.
Consider ceiling height when installing indoors – you’ll need adequate space for lighting systems and ventilation. If setting up outdoors, factor in protection from extreme weather and ensure your structure can support the weight of water-filled components. A typical home system with four growing towers and a fish tank requires approximately 16-20 square feet of total space.
Always include a small work area for monitoring equipment and storing essential supplies. This maintenance zone should be about 2-3 square feet and easily accessible.
Optimizing Plant Growth in Vertical Towers
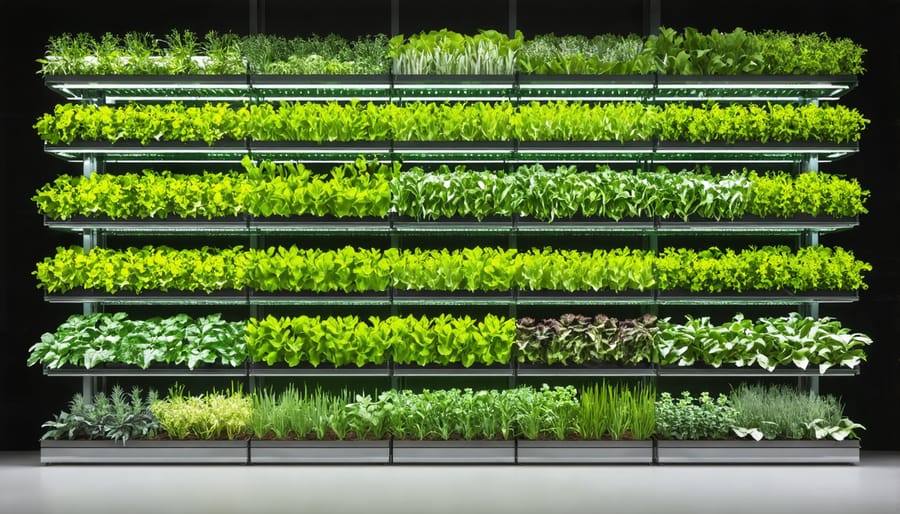

Plant Selection and Spacing
Selecting the right plants for your vertical aquaponic system is crucial for optimizing nutrient cycles and maximizing your growing space. Start with fast-growing, compact plants that thrive in water-rich environments. Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and kale are perfect beginners’ choices, as they have lightweight root systems and quick harvest cycles.
When planning your plant layout, consider the natural growth patterns and light requirements of each species. Taller plants should be positioned at the back or top of your system to prevent shading shorter ones. Allow about 6-8 inches between lettuce plants, 12 inches for medium-sized herbs, and 18-24 inches for larger plants like tomatoes or peppers.
For vertical systems, it’s smart to arrange plants in tiers based on their root depth. Place shallow-rooted plants like herbs and microgreens in upper levels, while keeping heavy feeders like tomatoes and cucumbers in lower tiers where they have more root space and won’t overshadow other plants.
Consider these tried-and-tested combinations:
– Top tier: Basil, mint, oregano
– Middle tier: Lettuce, spinach, Swiss chard
– Lower tier: Cherry tomatoes, bell peppers, compact bush beans
Remember to rotate your crops seasonally to prevent nutrient depletion and maintain system health. Start with just a few plant varieties and gradually expand as you gain experience. This approach helps you understand each plant’s specific needs and how they interact within your system.
To prevent overcrowding, regularly prune and harvest your plants. This not only maintains proper spacing but also encourages healthy growth and better air circulation, reducing the risk of plant diseases in your vertical setup.
Light Distribution Solutions
Getting light distribution right in your vertical aquaponic system is crucial for healthy plant growth. Since plants are arranged on different levels, you’ll need to be strategic about ensuring each one gets its fair share of light.
Natural sunlight is your best friend when it comes to lighting, but it needs proper management. Position your system where it can receive consistent light throughout the day, ideally facing south if you’re in the northern hemisphere. However, be mindful that lower-level plants might get shaded by those above them.
To solve this common challenge, consider these effective solutions:
Use reflective materials on nearby walls or surfaces to bounce light to shadowed areas. White paint or mylar sheets work great for this purpose. You can also install adjustable mirrors to direct sunlight to specific spots that need it most.
Space your growing levels appropriately – typically 12-18 inches apart works well for most plants. This spacing allows light to penetrate between levels and reaches plants on lower tiers. Consider arranging plants by height, with shorter varieties on upper levels and taller ones below.
For indoor systems or during darker months, supplemental lighting is often necessary. LED grow lights are energy-efficient and perfect for vertical systems. Mount them at different heights, focusing on areas that receive less natural light. Use adjustable arms or hanging systems so you can modify light positions as your plants grow.
Remember to rotate plants periodically, especially those on lower levels. This ensures all sides of the plant receive adequate light and develop evenly. Some gardeners use a simple tracking system – marking plants with dates to maintain a regular rotation schedule.
For the best results, monitor your plants closely for signs of insufficient light, such as leggy growth or pale leaves. Adjust your lighting strategy accordingly, and don’t be afraid to experiment with different arrangements until you find what works best for your specific setup.
Fish Management for Peak Performance
Stocking Density Guidelines
Getting the right balance of fish to plants is crucial for a successful vertical aquaponics system. A good starting point is to maintain 1 pound of fish for every 7 gallons of water in your system. For beginners, tilapia are excellent choices, and you can stock them at a rate of 1 fish per 3 square feet of growing space.
To maximize your system’s efficiency, consider these density guidelines:
– Small systems (under 100 gallons): 20-30 fish
– Medium systems (100-500 gallons): 40-75 fish
– Large systems (500+ gallons): 100+ fish
Remember that fish size matters too. As your fish grow, you’ll need to adjust their numbers. Start with fingerlings (young fish) and gradually reduce the population as they mature. A good rule of thumb is to begin with twice as many fingerlings as your target adult population, accounting for potential losses.
For plant density, follow these recommendations per square foot:
– Leafy greens: 4-8 plants
– Herbs: 4-6 plants
– Fruiting plants: 1-2 plants
Monitor your system’s water quality closely when approaching maximum stocking densities. Signs of overcrowding include:
– Decreased dissolved oxygen levels
– Higher ammonia readings
– Stressed fish behavior
– Slower plant growth
Start conservatively and increase gradually as you gain experience. It’s better to understock initially and add more fish later than to risk system failure from overcrowding. Regular water testing and observation of both fish and plant health will help you find the perfect balance for your vertical aquaponics setup.

Water Quality Maintenance
Maintaining optimal water quality is crucial for the success of your vertical aquaponic system. Regular water quality testing helps you monitor essential parameters and keep your fish and plants healthy.
Start by checking pH levels daily, aiming for a range between 6.0 and 7.0, which suits both fish and plants. Use natural pH adjusters like food-grade calcium carbonate to raise pH or phosphoric acid to lower it. Monitor ammonia and nitrite levels weekly – these should always be close to zero for fish safety.
Temperature management is equally important. Most systems thrive between 68-75°F (20-24°C). Install a reliable thermometer and consider using a small heater during colder months. Remember, sudden temperature changes can stress your fish.
Dissolved oxygen is vital for both fish and beneficial bacteria. Ensure proper aeration through air stones and maintain good water flow throughout your vertical system. Watch for signs of low oxygen, such as fish gasping at the surface.
Keep an eye on water clarity and remove any floating debris regularly. Top up water levels as needed, using dechlorinated water to replace what’s lost through evaporation and plant uptake. A well-maintained system should have minimal algae growth.
Pro tip: Keep a logbook to track your water parameters. This helps you spot trends and address potential issues before they become problems. Clean mechanical filters monthly and avoid using harsh chemicals that could harm your system’s beneficial bacteria.
System Monitoring and Maintenance

Daily and Weekly Tasks
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your vertical aquaponic system running smoothly. Here’s a simple checklist of tasks to perform daily and weekly to ensure your system thrives.
Daily Tasks:
– Check water temperature and pH levels (morning and evening)
– Monitor fish behavior and feeding patterns
– Remove any floating debris or dead plant matter
– Ensure all pumps are running correctly
– Look for signs of pest infestation or plant disease
– Check water flow in all growing sections
– Top up water levels if needed due to evaporation
Weekly Tasks:
– Test water quality (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels)
– Clean or rinse mechanical filters
– Focus on maintaining biofilters for optimal nutrient conversion
– Prune plants and remove any yellowing leaves
– Check and adjust plant spacing as needed
– Clean any salt buildup around water outlets
– Inspect plumbing for leaks or blockages
– Review fish health and growth
– Clean any algae buildup on surfaces
– Check and clean air stones if using additional aeration
Remember to keep a maintenance log to track system parameters and spot trends early. This helps you identify potential issues before they become problems. Spending just 15-20 minutes daily on these tasks can prevent major headaches down the line and ensure your system remains productive year-round.
Consider setting up automatic reminders on your phone for daily checks and scheduling longer maintenance sessions during weekends when you have more time available. Your consistent attention to these tasks will reward you with healthy fish and abundant plant growth.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best-maintained vertical aquaponic systems can encounter issues, but most are easily resolved with the right approach. One common challenge is uneven water flow, which can be fixed by adjusting pump pressure or clearing any blockages in the distribution pipes. If you notice some plants receiving more water than others, check the drip emitters and clean or replace them as needed.
Yellowing leaves often indicate nutrient deficiencies. In most cases, this can be resolved by adjusting the fish-to-plant ratio or supplementing with organic nutrients. Remember that new systems need time to establish beneficial bacteria, so patience is key during the first few weeks.
Fish health problems typically stem from poor water quality. Regular testing is essential – if ammonia or nitrite levels spike, reduce feeding temporarily and consider adding more plants to help filter the water. If you notice fish gasping at the surface, check oxygen levels and ensure your air stones are functioning properly.
Root rot can occur in systems with inadequate drainage or poor aeration. Improve air circulation around the roots by adjusting growing media or adding air gaps in your vertical towers. For systems experiencing algae growth, reduce light exposure to the water components and ensure all pipes and reservoirs are properly covered.
Temperature fluctuations can stress both plants and fish. Install shade cloth during hot summers and consider using insulation materials during colder months. If your system is outdoors, monitor weather forecasts and take preventive measures accordingly.
pH imbalances are easily corrected with natural buffers like crushed coral or food-grade limestone. Always make adjustments gradually to avoid shocking the system.
Embarking on your vertical aquaponics journey is an exciting step toward sustainable, space-efficient gardening that combines the best of aquaculture and hydroponics. As we’ve explored throughout this guide, these innovative systems offer a practical solution for growing fresh produce and raising fish in even the smallest spaces.
Remember that success in vertical aquaponics comes from understanding the fundamental relationship between fish, plants, and beneficial bacteria. Start small, monitor your system carefully, and adjust as needed. The beauty of vertical aquaponics lies in its flexibility – you can always expand or modify your setup as you gain confidence and experience.
The key takeaways from our discussion include the importance of proper system design, maintaining optimal water quality, selecting compatible fish and plant combinations, and establishing efficient nutrient cycling. Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial, but don’t let this intimidate you – most systems become quite stable once properly established.
Whether you’re looking to grow fresh herbs for your kitchen, create a living wall of leafy greens, or establish a small-scale food production system, vertical aquaponics offers a rewarding way to contribute to sustainable agriculture while enjoying the benefits of home-grown food.
We encourage you to take the plunge and start your own vertical aquaponics system. Begin with thorough planning, gather your materials, and don’t be afraid to learn through trial and error. The aquaponics community is supportive and always willing to share experiences and advice. With patience, attention to detail, and the knowledge you’ve gained from this guide, you’re well-equipped to create a thriving vertical aquaponics system that will provide fresh, healthy produce for years to come.
