
Keep Your Pond Safe: Essential Water Treatment Practices That Actually Work
Water treatment plant safety demands unwavering attention to protect both workers and public health. Every day, these facilities process millions of gallons of water while handling powerful chemicals and complex machinery. Proper safety protocols aren’t just regulatory requirements—they’re essential safeguards that prevent accidents, maintain water quality, and ensure continuous operation of these vital facilities.
From chlorine gas monitoring to confined space entry procedures, treatment plant operators must master multiple safety disciplines. Recent industry data shows that facilities with comprehensive safety programs experience 65% fewer workplace incidents and maintain higher water quality standards. Yet despite technological advances, human vigilance remains the cornerstone of treatment plant safety.
This guide explores critical safety measures every water treatment facility should implement, covering personal protective equipment, chemical handling protocols, emergency response procedures, and preventive maintenance strategies. Whether you’re a veteran operator or new to the field, these proven practices will help create a safer, more efficient working environment while ensuring the delivery of clean, safe water to your community.
Understanding Your Pond’s Water Chemistry
Essential Water Parameters to Monitor
Maintaining proper water parameters is crucial for the safety and efficiency of your water treatment system. Let’s look at the four most important parameters you should monitor regularly:
pH levels should stay between 6.8 and 7.2 for optimal treatment effectiveness. Test your water’s pH at least weekly using reliable test strips or a digital meter. Sudden changes in pH can indicate serious system issues that need immediate attention.
Ammonia levels must remain below 0.5 parts per million (ppm). High ammonia often signals inadequate filtration or overcrowding issues. Test for ammonia twice weekly, especially during warmer months when levels can spike quickly.
Nitrite readings should stay below 0.25 ppm. Often called “the silent killer,” nitrites can harm aquatic life and indicate poor biological filtration. Monitor nitrites alongside ammonia tests to ensure your system is functioning properly.
Dissolved oxygen is essential for healthy water treatment, with ideal levels between 6-8 ppm. Low oxygen can lead to system failure and harmful bacterial growth. Install an air pump or fountain to maintain proper oxygen levels, especially during hot weather when oxygen naturally decreases.
Remember to keep a log of all your readings to track trends and spot potential problems early.
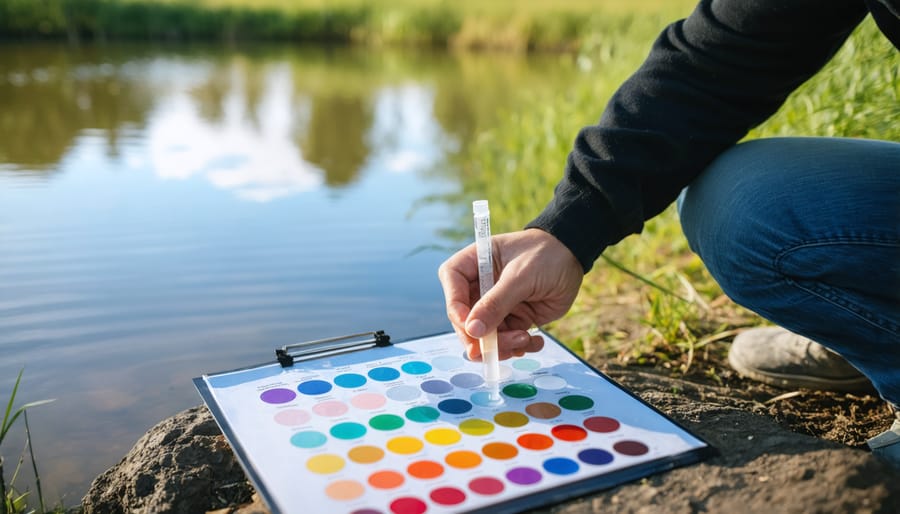
Safe Testing Methods for Home Ponds
Testing your home pond’s water quality doesn’t have to be complicated or dangerous. Start by using reliable water testing methods like digital meters or test strip kits, which are both safe and user-friendly. Always wear protective gloves when handling testing equipment and keep test materials away from children and pets. For best results, collect water samples from different pond areas using clean containers, and test during the morning hours before significant sun exposure. Remember to rinse all testing equipment with clean water after use and store test kits in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. If you’re unsure about readings, many local garden centers offer free water testing services as a safer alternative to home testing.

Chemical Treatment Safety
Choosing Safe Treatment Products
When selecting safe treatment products for your water treatment plant, it’s essential to match the solution to your specific pond issues. For algae control, look for products containing natural ingredients like barley extract or beneficial bacteria that won’t harm fish or plants. If dealing with pH imbalances, choose gradual pH adjusters rather than harsh chemicals that could shock your ecosystem.
Always check product labels for EPA registration and safety certifications. Consider the size of your pond when calculating dosage – using too much product can be as harmful as using too little. For bacterial issues, select broad-spectrum treatments that target harmful bacteria while preserving beneficial microorganisms.
Keep a log of which treatments work best for your pond and note any adverse reactions. Some products work better in certain seasons or temperatures, so timing matters. When in doubt, start with the minimum recommended dose and monitor results before adding more. Remember that natural, preventative solutions are often safer than reactive treatments for long-term pond health.
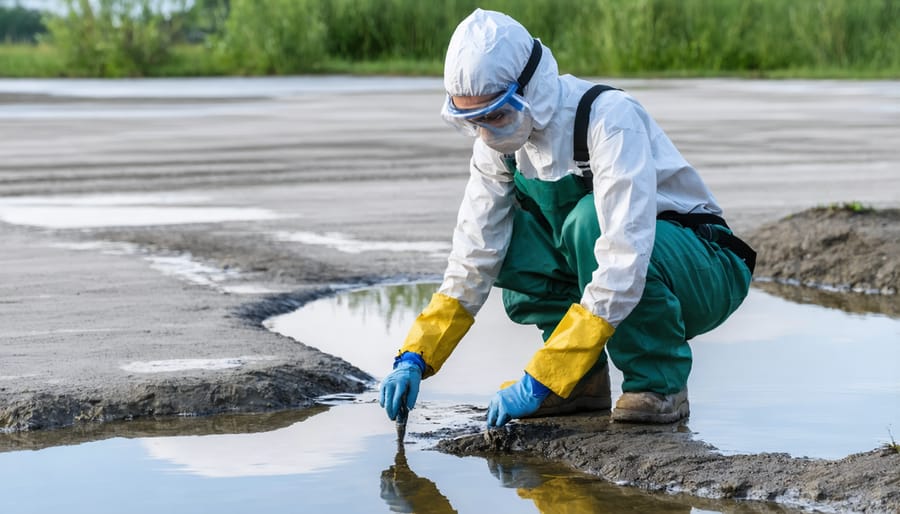

Personal Protection During Treatment
When working with pond chemicals and treatments, proper protection is essential for your safety. Always wear chemical-resistant gloves to prevent direct skin contact with treatment products. Safety goggles or a face shield protect your eyes from splashes and fumes that could cause irritation or injury.
Wear appropriate clothing, including long sleeves and closed-toe shoes, to minimize skin exposure. A protective apron or coveralls provide an extra layer of protection when handling stronger chemicals. If using products that release fumes, consider wearing a face mask or respirator rated for chemical vapors.
Keep clean water and an eye wash station nearby in case of accidental exposure. Store your safety gear in a clean, dry place away from chemicals, and inspect it regularly for wear and tear. Replace any damaged items immediately.
Remember to wash your hands thoroughly after handling treatments, even if you’ve worn gloves. Never eat, drink, or smoke while working with pond chemicals, and always work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
Natural Filtration Safety
Maintaining Filter Systems
Regular maintenance of biological filters is crucial for both system efficiency and operator safety. Always wear appropriate protective gear, including waterproof gloves and eye protection, before handling filter media. When cleaning, avoid disturbing beneficial bacteria colonies by gently rinsing media in pond water rather than tap water.
Never attempt to clean filters alone – always have a buddy system in place. Before opening filter housings, release pressure gradually and ensure proper ventilation to prevent exposure to harmful gases that may have built up. Keep your face away from filter openings when first removing covers.
Establish a regular cleaning schedule based on your system’s needs, typically every 3-6 months. Monitor pressure gauges and flow rates to identify when cleaning is necessary. After maintenance, check all seals and connections before restarting the system.
Document all maintenance activities and any issues encountered. This helps track patterns and prevents potential safety hazards from developing over time.
Beneficial Bacteria Management
Beneficial bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining healthy pond water, but they must be handled safely and added correctly. Always wear protective gloves when measuring and applying bacterial treatments, as some concentrated formulas can cause skin irritation. Store bacterial products in a cool, dark place between 40-80°F (4-27°C) to maintain their effectiveness.
When adding beneficial bacteria, start with a clean measuring cup dedicated to pond use. Pour the recommended amount into the pond near the water flow, such as near a waterfall or pump return, to help distribute the bacteria evenly. For best results, add bacteria in the morning or evening when water temperatures are moderate. If you’re handling water quality emergencies, double-check dosage calculations and never exceed recommended amounts, as over-treatment won’t speed up results.
Keep bacterial products away from children and pets, and always wash your hands thoroughly after application. Label all measuring tools clearly to prevent cross-contamination with other pond chemicals.
Emergency Response Plans
Identifying Water Quality Issues
Keeping a watchful eye on water quality is crucial for plant and operator safety. Watch for warning signs like unusual odors, particularly rotten egg or chlorine smells, which could indicate chemical imbalances. Discolored water, especially if it appears brown, green, or milky, demands immediate attention. Pay attention to any floating debris, oily films, or excessive foam on the water surface.
If you notice these issues, your first step should be to verify all monitoring equipment is working correctly. Check pH levels, turbidity readings, and chlorine levels immediately. Document your findings and compare them with normal operating parameters. If readings are outside safe ranges, follow your facility’s emergency response procedures.
Always alert supervisors to potential problems and never attempt to correct major issues alone. Keep emergency contact numbers readily available, and ensure all team members know the proper reporting procedures for water quality concerns.
Safe Emergency Procedures
In case of a water emergency, follow these essential steps to ensure safety and minimize damage. First, immediately shut off the main power supply to all electrical equipment near the water. If you notice unusual water color or smell, evacuate the area and ensure proper ventilation.
For chemical spills, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection if necessary. Contain the spill using absorbent materials and follow your facility’s spill response protocol. Never mix unknown chemicals or attempt to neutralize them without proper knowledge.
If equipment malfunctions, engage the emergency stop systems and alert all personnel in the vicinity. Keep emergency contact numbers clearly posted and easily accessible. Always maintain clear access to emergency exits and safety equipment.
For overflow situations, activate containment systems and notify relevant authorities. Document all incidents and maintain an updated emergency response plan that includes evacuation routes and assembly points.
Remember, prevention is key – regular maintenance and safety checks can help avoid many emergency situations.
Maintaining a safe water treatment system is essential for the health of your pond and its inhabitants. By following the safety guidelines we’ve discussed, you can create a thriving aquatic environment while protecting yourself and others. Remember to regularly check all electrical connections, maintain proper chemical storage, and keep safety equipment readily accessible. Make it a habit to inspect your system weekly, paying special attention to pump functions, filter conditions, and water quality parameters.
Don’t forget to keep a maintenance log and schedule routine professional inspections at least annually. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Create and review your emergency response plan periodically, ensuring all family members or staff know what to do in case of equipment failure or chemical exposure.
Most importantly, never skip safety protocols, even for quick maintenance tasks. A few extra minutes of preparation can prevent accidents and ensure your water treatment system operates efficiently for years to come. By making safety a priority, you’ll enjoy peace of mind while maintaining your beautiful aquatic environment.
