
Aquaponics Made Easy: Step-by-Step DIY System Setup
Here are 3 actionable steps to build your own aquaponics system:
1. Gather the essential components: a fish tank, grow bed, water pump, air pump, grow medium (like clay pebbles), and PVC pipes. Size the tank and grow bed based on the fish and plants you want to raise.
2. Assemble the system by connecting the fish tank to the grow bed using the water pump and PVC pipes. Fill the grow bed with the medium. Install the air pump in the fish tank for oxygenation.
3. Cycle the system by adding ammonia to start building beneficial bacteria. After 3-6 weeks, add fish and plant seedlings. Feed the fish and monitor water quality daily. Harvest and enjoy!
With planning, the right materials, and regular upkeep, you’ll be enjoying fresh homegrown produce and fish in no time. Roll up your sleeves and dive into this rewarding, sustainable hobby today!

Gather Materials
Fish Tank
The size of your fish tank depends on the number and type of fish you plan to raise. For a small aquaponics system, a 50-100 gallon tank is usually sufficient. Choose a sturdy, food-grade plastic or fiberglass tank that can withstand the weight of water and fish. Avoid using metal tanks, as they can rust and leach harmful substances into the water. When selecting fish, consider species that are well-suited to aquaponics, such as tilapia, catfish, or trout. These fish are hardy, fast-growing, and can thrive in the unique conditions of an aquaponics system. Make sure to provide adequate space, filtration, and aeration for your chosen fish to ensure their health and well-being.
Grow Bed
The grow bed is where your plants will thrive in the aquaponics system. Choose a durable, food-safe material like a plastic container or a lined wooden bed. Ensure the grow bed is at least 12 inches deep to accommodate plant roots and growing media. Lightweight expanded clay aggregate (LECA) or gravel work well as growing media, providing excellent drainage and surface area for beneficial bacteria. Position the grow bed above the fish tank, allowing the nutrient-rich water to flow through the media and back into the tank. Include a bell siphon or overflow drain to regulate water levels and prevent flooding.
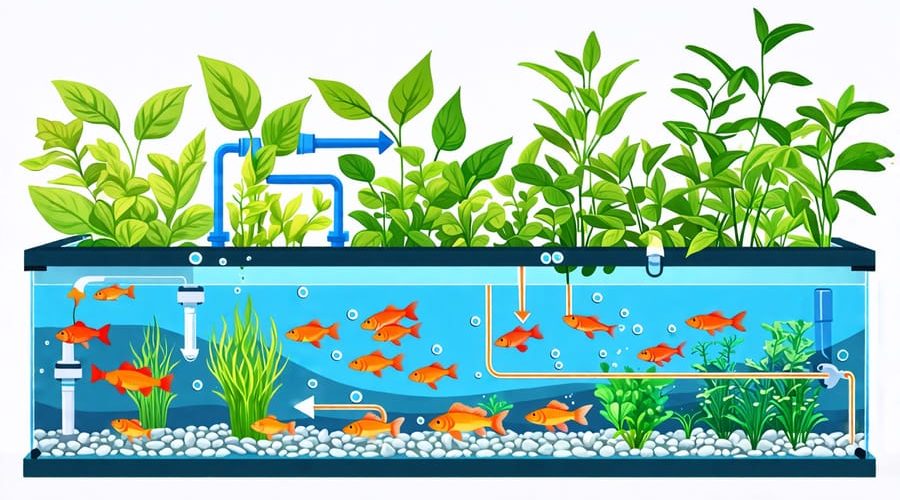
Plumbing Components
To build your aquaponics system, you’ll need a reliable pump to circulate water between the fish tank and grow bed. Choose a submersible or inline pump based on your system size. PVC pipes and fittings connect the components, with pipe diameter depending on pump output. Include a checkvalve to prevent backflow. Bulkhead fittings securely connect pipes to the fish tank and grow bed. Consider adding ball valves for flow control. Ensure all connections are watertight to avoid leaks. With the right plumbing setup, your aquaponics system will efficiently cycle water and nutrients for optimal plant growth and fish health.

Assemble the System
Install the Fish Tank
Setting up your fish tank is an exciting step in building your aquaponics system. First, choose a location that can support the weight of a filled tank and is close to electrical outlets. Carefully place your tank on a sturdy, level surface. If needed, use shims to ensure it’s perfectly balanced. Seal any leaks with aquarium-safe silicone sealant.
Install the filtration system according to the manufacturer’s instructions, securing all hoses and connections. Add your chosen substrate, such as gravel, then fill the tank with dechlorinated water. Let the water cycle for a few days to allow beneficial bacteria to establish.
When the water parameters are stable, it’s time to add your fish! Choose species that thrive in the tank’s environment and are compatible with your plants. Acclimatize them slowly by floating the bag in the tank water for about 15 minutes before releasing them. Monitor your new aquatic residents closely and maintain proper water quality for their health and happiness.
Prepare the Grow Bed
To prepare the grow bed for your aquaponics system, start by filling it with a lightweight growing medium such as expanded clay pebbles or perlite. These materials provide excellent drainage and aeration for plant roots. Rinse the growing medium thoroughly to remove any dust or debris before adding it to the bed.
Next, create a slight slope in the grow bed to ensure proper water flow and drainage. This can be achieved by adding more growing medium to one end of the bed. Install a bell siphon or standpipe to regulate the water level and prevent overflow.
Before planting, test the pH level of the growing medium and adjust it to a range of 6.5 to 7.0, which is suitable for most aquaponic plants. You can use natural additives like limestone or oyster shells to raise the pH if needed.
Finally, consider installing a removable cover or net over the grow bed to protect your plants from pests and excessive sunlight. With your grow bed prepared, you’re ready to start planting your favorite herbs, vegetables, or leafy greens in your aquaponics system.
Connect the Plumbing
Now that your grow beds and fish tanks are in place, it’s time to connect the plumbing to create a continuous water flow between the components. Start by attaching a submersible pump to the bottom of your fish tank. This pump will circulate the nutrient-rich water from the fish to the grow beds. Use flexible PVC piping to connect the pump outlet to the grow bed inlet, ensuring a watertight seal at each connection point.
Next, install an overflow drain at the desired water level in your grow beds. This allows the water to drain back into the fish tank once it reaches a certain height. Connect the overflow drain to a return pipe that leads back to the fish tank, completing the water cycle.
To maintain optimal water quality, consider adding a filtration system between the fish tank and grow beds. A simple swirl filter or settling tank can help remove solid waste before the water reaches your plants. Additionally, installing an aerator in the fish tank will provide your fish with the oxygen they need to thrive.
Test your plumbing for leaks by running water through the system and making adjustments as necessary. With your plumbing in place, you’re one step closer to enjoying the benefits of your very own aquaponics system!
Cycling the System
The nitrogen cycle is the heart of any aquaponics system, converting fish waste into nutrients for plants. To establish this cycle in your new setup, you’ll need to “cycle” the system by introducing ammonia and allowing beneficial bacteria to grow. Start by adding a few hardy fish to your tank. As they produce waste, ammonia levels will rise. Next, introduce ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, which convert ammonia into nitrites. These bacteria will naturally develop, but you can speed up the process with commercial additives. As nitrites build up, nitrite-oxidizing bacteria will convert them into nitrates, which plants readily absorb. Monitor ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels with test kits. Ammonia and nitrite should eventually reach zero, while nitrates will rise. This process typically takes 4-6 weeks. During this time, perform regular water changes and avoid adding too many fish. Once the cycle is established, you can gradually increase fish numbers and add a wider variety of plants. Remember, patience is key when cycling your aquaponics system. Rushing the process can lead to imbalances and harm your fish and plants. With proper monitoring and maintenance, you’ll soon have a thriving, self-sustaining ecosystem that produces fresh, healthy food for your home.
Add Fish and Plants
Choosing Fish
When choosing fish for your aquaponics system, consider species that are hardy, adaptable to varying water conditions, and well-suited for tank life. Tilapia is a popular choice due to its fast growth rate, disease resistance, and ability to thrive in diverse environments. Other excellent options include catfish, trout, perch, and bass. Keep in mind the temperature requirements of each species and whether they are compatible with the plants you intend to grow.
It’s crucial to strike a balance between the number of fish and the size of your tank to maintain a healthy ecosystem. As a general rule, aim for one pound of fish per 5-10 gallons of water. Begin with a smaller number of fish and gradually increase the population as your system matures. Regularly monitor water quality, fish health, and plant growth to ensure optimal conditions and make adjustments as needed.
Planting Techniques
When planting in your aquaponics grow bed, start by choosing plants well-suited to this unique environment, such as leafy greens, herbs, and small fruiting plants. Seedlings are typically easier than starting from seeds. Gently remove the plant from its container, being careful not to damage the roots. Create a small hole in the grow media, place the plant, and carefully fill in around it, providing support as needed. Space plants according to their mature size, ensuring adequate room for growth. Avoid overcrowding, which can hinder plant development and make maintenance challenging. Monitor your plants closely, especially in the early stages, watching for signs of stress or nutrient deficiencies. Adjust your system as needed, such as tweaking the water flow or adding supplemental nutrients. With proper care and attention, your aquaponics plants will thrive, providing you with a bountiful harvest of fresh, healthy produce.
System Maintenance
Water Quality
Monitoring and maintaining optimal water quality is crucial for the health of your aquaponics system. Regularly test pH levels, which should be between 6.8 and 7.0 for most plants and fish. Ammonia and nitrite levels should be kept near zero, while nitrate levels can be around 5-150 ppm depending on the plants you’re growing. To maintain these parameters, perform regular water filtration, such as removing solid waste and replacing 10-20% of the water weekly. Keep an eye out for signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities in your plants, which can indicate imbalances in the water. Adjust your feeding and filtration routine as needed to keep the system in balance. Investing in a quality water testing kit and learning to interpret the results will help you keep your aquaponics system thriving.
Fish Care
Ensuring the health and well-being of your fish is crucial for a thriving aquaponics system. Feed your fish a balanced diet specifically formulated for their species, following the recommended feeding schedule. Observe their behavior and appetite, as changes can indicate potential health issues. Regularly monitor water quality parameters such as temperature, pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, making adjustments as needed. Maintain proper stocking densities to prevent overcrowding and stress. Remove any uneaten food and debris to prevent water quality deterioration. Periodically inspect your fish for signs of disease or parasites, and address any issues promptly with appropriate treatments. By providing optimal living conditions and a balanced ecosystem, you’ll not only keep your fish healthy but also create a wildlife habitat that supports the natural cycle of your aquaponics system.
Plant Health
Monitoring your plants’ health is crucial for a thriving aquaponics system. Regularly inspect leaves for discoloration, wilting, or unusual spots, which may indicate nutrient deficiencies or pest issues. Yellow leaves often signal a lack of iron or nitrogen, while curling leaves may point to calcium deficiency. If you notice pests like aphids or whiteflies, consider natural remedies like neem oil or ladybugs before resorting to chemical treatments. Prune away any damaged or diseased foliage to prevent spread. Maintain optimal water quality and pH levels to support plant health. With attentive care and quick action when issues arise, your aquaponics plants will flourish.
