
Keep Your Pond Thriving: Smart Climate Resilience Strategies That Work
Protect your pond’s long-term health by developing a comprehensive climate resilience plan today. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and shifting rainfall patterns pose unprecedented challenges for pond owners – but with strategic preparation, your water feature can thrive despite these environmental pressures.
Climate resilience planning combines proactive infrastructure improvements, ecosystem management, and emergency preparedness to create robust water features that withstand weather extremes. From installing overflow systems that handle flash floods to selecting drought-resistant plants that stabilize banks, each protective measure builds upon the next to form a complete defense system.
The key to successful climate adaptation lies in understanding your pond’s unique vulnerabilities and implementing targeted solutions. By assessing factors like watershed position, soil composition, and existing plant communities, you can identify potential weak points and strengthen them before problems arise. This guide will walk you through creating a customized resilience strategy that safeguards your pond investment while preserving its natural beauty and ecological functions for years to come.
Let’s explore practical steps to climate-proof your pond, starting with essential infrastructure upgrades that provide immediate protection against severe weather impacts.
Understanding Climate Threats to Your Pond
Temperature Fluctuations
Temperature swings can dramatically impact your pond’s ecosystem, making managing extreme temperatures crucial for long-term success. During heat waves, warm water holds less oxygen, potentially stressing fish and promoting excessive algae growth. Cold snaps can be equally challenging, as ice formation might trap harmful gases and prevent vital gas exchange at the water’s surface. Your plants and fish have adapted to survive seasonal changes, but sudden or extreme fluctuations can overwhelm their natural resilience. Watch for signs of stress like fish gasping at the surface during hot spells or clustering near the bottom in cold weather. Understanding these temperature-related challenges helps you take proactive steps to protect your pond family, whether it’s adding shade during summer or maintaining a small ice-free area in winter.
Drought and Water Loss
Climate change brings increased risks of drought and water loss to pond environments, making it crucial to implement protective measures. To prevent water loss, consider installing shade sails or adding floating plants like water lilies to reduce evaporation. Adding a deeper section to your pond (at least 2-3 feet) helps maintain stable water levels during dry spells. Regular monitoring of water levels and having a backup water source ready are essential practices. Installing an efficient recirculation system and maintaining proper filtration can help conserve water while keeping your pond healthy. During drought periods, reduce water features like fountains and waterfalls to minimize evaporation, and consider collecting rainwater in barrels for emergency top-ups.

Storm Damage and Flooding
Heavy storms and flooding can wreak havoc on your pond, but with proper planning, you can minimize potential damage. Install overflow pipes or spillways to safely direct excess water away from your pond during heavy rainfall. Consider adding a berm or raised edge around your pond to prevent surrounding floodwater from rushing in and contaminating your water.
Keep an eye on your pond’s banks and edges during storms. Stabilize these areas with deep-rooted plants or stone reinforcement to prevent erosion. If possible, create a rain garden nearby to help absorb excess water and reduce flooding pressure on your pond.
During severe weather events, remove valuable equipment and decorative features that could be damaged or swept away. Have a backup power source ready for essential pumps and filtration systems to maintain water quality even during extended power outages. Regular maintenance of drainage systems and keeping them clear of debris will help ensure they function properly when you need them most.
Building Your Pond’s Natural Defenses
Strategic Plant Selection
Choosing the right plants for your pond can make all the difference in creating a climate-resilient water garden. Focus on native aquatic plants that have naturally adapted to your local weather patterns and temperature fluctuations. These plants typically require less maintenance and are better equipped to handle extreme weather events.
Consider incorporating deep-rooted marginal plants like rushes and sedges along your pond’s edges. These plants help stabilize banks during heavy rains and provide natural filtration. Water lilies are excellent choices for temperature regulation, as their floating leaves shade the water and reduce evaporation during hot spells.
Look for plants that can tolerate both drought and flooding conditions. Cattails and iris species are particularly hardy choices, while submerged plants like hornwort and water milfoil help maintain water quality even during temperature swings. For areas prone to drought, consider including moisture-loving plants that can survive periodic dry spells, such as marsh marigolds and cardinal flowers.
Remember to create different planting zones within your pond. Include shallow marginal plants, deep-water plants, and floating varieties to establish a balanced ecosystem. This diversity not only enhances your pond’s resilience but also provides various habitats for wildlife, contributing to a healthier, more stable water feature that can better withstand climate challenges.
Avoid invasive species at all costs, as these can become particularly aggressive during climate stress and overwhelm native plants. Instead, work with local nurseries to identify region-specific varieties that have proven track records in your area’s climate conditions.
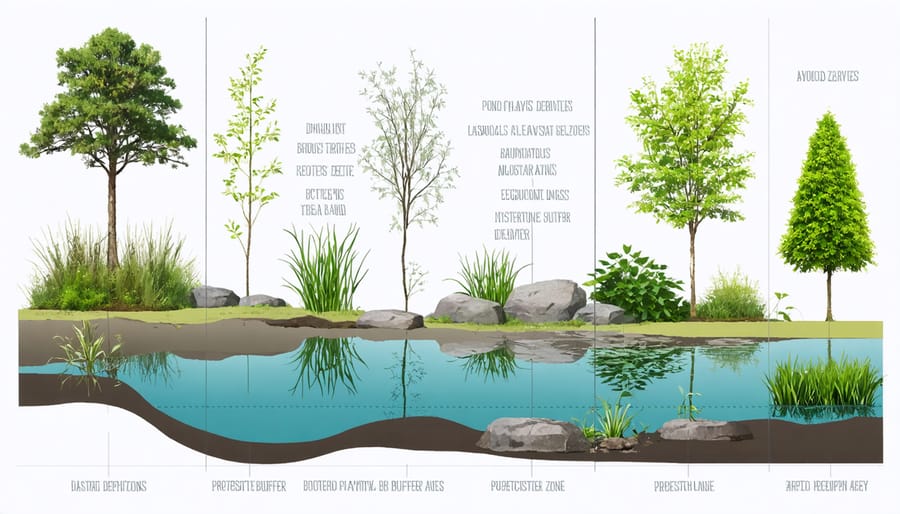
Creating Buffer Zones
Creating buffer zones around your pond is one of the most effective ways to protect it from climate-related challenges. Think of these zones as protective shields that help your pond weather various environmental stresses while adding beauty to your landscape.
Start by establishing a vegetation strip at least 3-5 feet wide around your pond’s perimeter. Choose native plants with deep root systems, as they’re naturally adapted to your local climate and can help prevent soil erosion during heavy rains. Consider layering your buffer with different plant heights – tall grasses at the back, medium-sized perennials in the middle, and ground covers near the water’s edge.
Adding rock borders or natural berms within your buffer zone creates additional protection against runoff and helps direct excess water away from your pond during storms. These features also provide hiding spots for beneficial wildlife and help maintain water temperature stability.
For slopes leading to your pond, consider terracing the buffer zone to slow water flow and prevent soil washing into your pond. Plant each terrace level with different species to create a living retaining wall that’s both functional and attractive.
Remember to maintain your buffer zone regularly by removing invasive plants, replacing damaged vegetation, and ensuring the protective features remain intact. A well-maintained buffer zone not only protects your pond but also creates a beautiful transition between your water feature and the surrounding landscape.
Water Depth Planning
Creating different depth zones in your pond is crucial for maintaining stable temperatures and supporting resilient ecosystems. Understanding these essential pond zones helps your water feature better withstand climate fluctuations.
The shallow margin zone (0-12 inches deep) acts as a thermal buffer, warming quickly but also cooling rapidly. While this area is perfect for marginal plants, it’s important not to make too much of your pond this depth, as it can lead to temperature instability.
The middle zone (12-24 inches) provides an ideal compromise between temperature stability and plant growth. This depth maintains relatively consistent temperatures while allowing enough light penetration for submerged plants to thrive.
The deep zone (24-36 inches or more) is your pond’s temperature anchor. This area stays cooler in summer and warmer in winter, creating a refuge for fish and other aquatic life during extreme weather. Aim to make at least 30% of your pond this depth for optimal climate resilience.
When planning these zones, consider creating gradual slopes rather than sharp drops. This natural transition helps circulate water between temperature zones and prevents stagnant areas. Remember that deeper water requires less frequent maintenance and provides better protection against both freezing and overheating.
Tech Solutions for Climate Protection
Water Quality Monitoring
Regular water quality monitoring is your first line of defense in maintaining a climate-resilient pond. Think of it as taking your pond’s vital signs – it helps you spot potential problems before they become serious issues. The key parameters to track include dissolved oxygen levels, pH, temperature, and nutrient concentrations.
Start by testing your water weekly during warm months and bi-weekly during cooler periods. Many pond owners find that early morning readings give the most accurate picture of their pond’s health. Use a reliable water testing kit that measures all essential parameters, and keep a log of your readings to track changes over time.
Temperature monitoring is particularly crucial as climate change brings more extreme weather events. Install a floating thermometer or digital temperature probe in your pond’s deepest section. Sudden temperature swings can stress fish and encourage algae growth, so having this data helps you take preventive action.
Invest in a dissolved oxygen meter to ensure your pond maintains healthy oxygen levels, especially during heat waves. If levels drop, you can quickly respond by adding an aerator or surface agitator. For pH monitoring, aim to keep levels between 6.5 and 8.5, adjusting with appropriate treatments when needed.
Create a simple spreadsheet or use a pond management app to record your measurements. This data becomes invaluable for identifying patterns and making informed decisions about pond management. Remember that prevention is always easier than cure – regular monitoring helps you maintain optimal conditions and adapt your management strategies as climate patterns change.
Consider installing automated monitoring systems if your budget allows. These provide real-time alerts when parameters drift outside acceptable ranges, giving you peace of mind and faster response times to potential problems.

Temperature Management Systems
Temperature fluctuations can be tough on pond life, but there are several effective ways to manage water temperatures throughout the year. For smaller ponds, floating pond coolers work like giant ice packs, helping to lower water temperatures during heat waves. These are especially useful for koi ponds, where fish are sensitive to sudden temperature changes.
Pond fountains and aerators serve double duty by not only adding beautiful movement to your water feature but also helping regulate temperature. The water movement prevents stratification, where different temperature layers form in the pond, and helps maintain consistent oxygen levels throughout.
For year-round temperature management, consider installing a pond heater or de-icer for winter months. These devices prevent complete surface freezing, allowing vital gas exchange to continue even in freezing conditions. Remember to position heaters away from liner materials to prevent damage.
Shade solutions offer natural temperature control. Floating plants like water lilies provide coverage while adding beauty to your pond. Strategic placement of marginal plants around the pond’s edge can also create helpful shade patterns. For immediate results, shade sails or pergolas can be installed above particularly exposed areas.
Deep zones in your pond (at least 2-3 feet) act as natural temperature buffers, giving fish and other pond life a retreat during extreme weather. When planning new ponds or renovating existing ones, incorporating these deeper areas should be a priority for climate resilience.
Monitor your pond’s temperature regularly using a reliable pond thermometer. This helps you spot concerning trends early and adjust your management strategy accordingly. Quick response to temperature changes can prevent stress on your pond’s ecosystem.
Emergency Response Planning
Creating Your Weather Action Plan
Start by assessing your pond’s specific vulnerabilities to different weather conditions. Create a checklist for each season, noting potential risks like heavy rain, drought, or extreme temperatures. Include essential weather-proofing strategies for each scenario.
For storm preparation, keep emergency supplies handy: backup pumps, water testing kits, and protective covers. During drought periods, plan water conservation methods like adding shade plants or installing rain barrels. For winter, outline steps for protecting fish and equipment from freezing.
Create an emergency contact list including local pond specialists and equipment suppliers. Document your pond’s normal water levels, chemical readings, and flow rates – this baseline helps you spot problems early. Take photos of your pond throughout the year to track changes and identify areas needing attention.
Review and update your action plan seasonally, making adjustments based on what works best for your specific setup. Remember to include regular maintenance tasks like debris removal and filter cleaning in your weather preparation routine.
Emergency Equipment Checklist
Every pond owner should maintain a well-stocked emergency kit to handle climate-related challenges. Start with basic weather protection items like heavy-duty tarps, sandbags, and UV-resistant pond netting to shield your pond from extreme conditions. Keep a battery-powered water pump handy for managing water levels during heavy rainfall or flooding.
Essential tools should include a long-handled net for debris removal, water testing kits to monitor quality changes, and basic repair supplies like waterproof tape and sealant. Don’t forget a reliable flashlight, battery-operated radio for weather updates, and a first-aid kit for both humans and fish.
For power outages, maintain a backup generator with enough fuel to run essential pond equipment for at least 72 hours. Store extra filters, replacement parts for pumps, and emergency fish food in a waterproof container. Having clean buckets and containers ready for temporary fish relocation can be crucial during severe weather events.
Keep important contact information readily available, including local wildlife services, veterinarians who treat fish, and nearby pond supply stores. Update your emergency kit seasonally and replace any expired items promptly.
Climate resilience planning isn’t just about preparing for the worst – it’s about ensuring your pond remains a thriving haven despite changing weather patterns. By taking steps now to assess risks, strengthen infrastructure, and implement protective measures, you’re investing in your pond’s long-term health and beauty. Remember to regularly monitor water levels, maintain backup systems, and keep emergency supplies ready. Creating a detailed action plan and staying informed about local climate trends will help you adapt quickly when needed. Most importantly, don’t wait for problems to arise – start your climate resilience journey today. With proper planning and preparation, your pond can continue to bring joy and tranquility to your outdoor space for years to come, regardless of what Mother Nature throws your way.
