
How Climate Change is Reshaping Your Pond’s Delicate Balance
As pond owners and water gardening enthusiasts, we’re witnessing firsthand how climate change reshapes our beloved aquatic ecosystems. From shifting water temperatures to unpredictable rainfall patterns, these changes directly impact the delicate balance we’ve worked so hard to maintain in our backyard water features.
Temperature fluctuations now push our pond inhabitants beyond their comfort zones more frequently than ever before. Fish that once thrived may show signs of stress, while algae blooms appear earlier and last longer. Native plants struggle to adapt to new seasonal rhythms, and non-native species increasingly compete for resources in our carefully planned water gardens.
But don’t let these challenges discourage you! Understanding how climate change affects our ponds empowers us to take proactive steps. By monitoring water quality more closely, selecting resilient plant species, and implementing adaptive maintenance strategies, we can help our aquatic ecosystems remain healthy and vibrant despite environmental changes.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical solutions to protect your pond from climate-related challenges, focusing on simple adjustments that make a big difference. Whether you’re dealing with excessive evaporation, unexpected pH changes, or stressed aquatic life, you’ll find actionable steps to maintain your pond’s balance in these changing times.
Temperature Changes: The First Domino to Fall
Water Temperature’s Impact on Fish Health
As our climate continues to warm, pond owners face increasing challenges in maintaining healthy environments for their fish. Water temperature plays a crucial role in fish health, affecting everything from their metabolism to their oxygen needs of fish in ways that might surprise you.
When water temperatures rise, fish become more active and their metabolism speeds up. Think of it like running a marathon in hot weather – your body needs more energy and oxygen to keep going. The same happens with fish, but they can’t simply slow down or take a break when things get too warm. This increased activity means they need more food and oxygen to survive, putting extra stress on their bodies.
The challenge doesn’t stop there. Warmer water naturally holds less dissolved oxygen, creating a double whammy effect. Just when fish need more oxygen due to their increased metabolism, there’s actually less available in the water. This can lead to visible signs of stress in your fish, such as gasping at the surface or becoming sluggish.
For pond owners, this means taking extra precautions during warm periods. Adding shade elements, maintaining proper water depth, and ensuring good circulation can help manage water temperatures. Installing an aerator or fountain can be a game-changer, helping to both cool the water and increase oxygen levels when your fish need it most.
Plant Life Under Pressure
As climate change intensifies, our beloved pond ecosystems face unprecedented challenges that directly impact aquatic plant growth patterns. Water temperatures are rising, creating a domino effect that affects everything from oxygen levels to nutrient availability. Many pond owners notice their water lilies blooming earlier in the season, while some submerged plants struggle to maintain their usual growth cycles.
These changes aren’t just about timing – they’re affecting plant survival rates too. Some floating plants might grow more aggressively in warmer conditions, potentially overwhelming your pond’s surface. Meanwhile, cooler-water species like hornwort might show signs of stress, with yellowing leaves or slower growth rates. The good news? Your pond plants are remarkably resilient and can adapt with proper care.
Keep an eye on your plants’ behavior – if you notice unusual patterns, it might be time to adjust your care routine. Consider adding shade plants around your pond to help regulate water temperature, and maintain consistent water levels during dry spells. Some pond owners have success with introducing new plant varieties that thrive in warmer conditions.
Remember, healthy plants are your pond’s best defense against climate challenges. They help maintain water quality, provide shelter for fish, and keep algae in check. By understanding these changes, you can better protect your pond’s plant life and maintain a thriving aquatic ecosystem.
The Water Level Challenge
Managing Drought Periods
During drought periods, ecosystems face significant challenges in maintaining water balance. To adapt and survive, many species develop specialized mechanisms. Plants may develop deeper root systems or modify their leaf structure to reduce water loss through transpiration. Some animals might alter their behavior patterns, becoming more nocturnal to avoid peak heat hours and conserve water.
Communities can help maintain ecosystem resilience through various water conservation strategies. Installing water-efficient irrigation systems, collecting rainwater, and implementing drought-resistant landscaping can help preserve local water resources. Creating wildlife corridors and protecting existing water bodies also helps species access water sources during dry spells.
Natural solutions like constructing wetlands and restoring riparian zones can act as water reserves during drought periods. These areas not only store water but also provide crucial habitat for various species. Additionally, maintaining healthy soil through organic matter addition improves water retention capacity and supports ecosystem function during dry periods.
Monitoring systems and early warning networks help communities prepare for and respond to drought conditions. This proactive approach allows for better resource management and helps protect vulnerable species and habitats. Regular assessment of water levels and ecosystem health indicators enables adaptive management strategies to be implemented effectively.
Heavy Rain Impacts
Heavy rainfall events are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change, posing significant challenges for ecosystems worldwide. When excessive rain falls in short periods, it can overwhelm natural drainage systems, leading to soil erosion, flooding, and nutrient runoff. This increased water flow carries pollutants and sediments into water bodies, disrupting aquatic ecosystems and threatening biodiversity.
In forest ecosystems, heavy rains can damage root systems and destabilize trees, particularly in areas already weakened by drought or disease. The excess water also affects soil chemistry, potentially washing away essential nutrients that plants need for growth. Some species may struggle to adapt to these rapidly changing conditions, while others might benefit from the increased moisture availability.
Urban ecosystems face unique challenges during heavy rain events. The abundance of impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt prevents natural water absorption, intensifying runoff issues. This can overwhelm storm drainage systems and create urban heat island effects, further stressing local flora and fauna.
Agricultural systems also suffer from heavy rain impacts, with crop damage, soil erosion, and delayed planting seasons becoming more common. These changes ripple through the food chain, affecting both wild and domesticated species that depend on these environments.
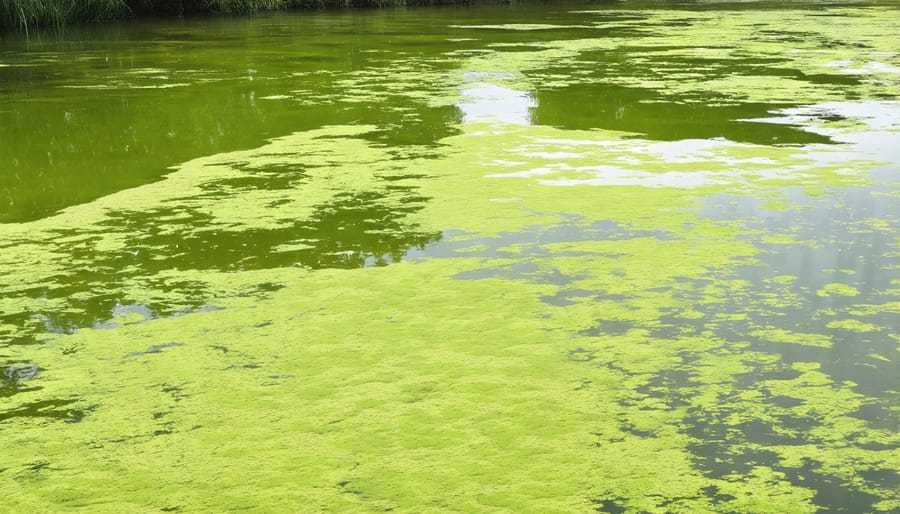

Algae Blooms: A Growing Concern
Natural Prevention Methods
As our climate continues to warm, maintaining ecological balance in water features becomes increasingly important. Fortunately, there are several effective ways to control algae growth naturally while supporting your pond’s ecosystem.
One of the most effective approaches is adding beneficial aquatic plants. Water lilies and floating plants provide essential shade, reducing water temperature and limiting sunlight that algae need to thrive. Submerged plants like hornwort and anacharis compete with algae for nutrients, naturally keeping their growth in check.
Creating a balanced ecosystem is key. Adding beneficial bacteria helps break down organic matter and compete with algae for nutrients. These helpful microorganisms work tirelessly to maintain water quality and prevent algae blooms. Consider installing a biofilter or adding barley straw, which releases compounds that naturally inhibit algae growth as it decomposes.
Physical solutions can make a big difference too. Installing a pond aerator or fountain increases oxygen levels and creates water movement, making it harder for algae to establish. Regular maintenance, like removing fallen leaves and debris, prevents excess nutrients from feeding unwanted algae growth.
Don’t forget about fish! Adding the right number of fish, particularly algae-eating varieties like grass carp or plecos, can help maintain balance. Just be careful not to overstock, as too many fish can contribute to water quality issues.
For immediate results, try using UV clarifiers, which use ultraviolet light to destroy single-celled algae as water passes through. This method is especially effective when combined with other natural approaches.
Remember to be patient – natural solutions take time to establish but provide long-term benefits for your pond’s health and appearance. By implementing these eco-friendly methods, you’ll create a resilient ecosystem that can better withstand climate-related challenges while staying beautiful and clear.
Protecting Your Pond’s Future
Smart Design Adaptations
As our climate continues to change, smart design adaptations can help your pond remain resilient and beautiful. Start by incorporating deeper sections in your pond – aim for at least 2-3 feet in depth. These deeper zones act as thermal refuges for fish and other aquatic life during extreme temperature swings, while also reducing water loss through evaporation.
Consider installing adjustable overflow systems that can handle both drought and heavy rainfall. A combination of traditional skimmers and raised spillways gives you flexibility to manage varying water levels throughout the year. Adding a bottom drain can help remove excess sediment that might accumulate during stronger storms.
Strategically placed plants play a crucial role too. Create graduated plant shelves at different depths, allowing vegetation to adapt as water levels fluctuate. Native marginal plants with deep root systems help stabilize banks and prevent erosion during heavy rains. Floating plants provide essential shade that keeps water temperatures stable and reduces evaporation.
Installing a reliable filtration system with UV clarification helps maintain water quality as temperatures rise. Consider adding an aeration system – it’s not just for winter anymore. Year-round aeration helps maintain healthy oxygen levels, especially important during hot spells when water naturally holds less dissolved oxygen.
Remember to incorporate easily accessible maintenance points around your pond. As weather patterns become less predictable, being able to quickly adjust or maintain your pond’s features becomes increasingly important.
Climate-Resilient Species Selection
When adapting your pond to climate change, selecting the right hardy plants and fish species is crucial for long-term success. Look for plants that can handle temperature swings and varying water levels. Water lilies are excellent choices, particularly tropical varieties that thrive in warmer conditions. Cattails and rushes are tough performers that help stabilize water temperatures and provide shelter for pond life.
For fish selection, consider species that adapt well to changing conditions. Goldfish are surprisingly resilient and can handle temperature fluctuations better than many fancy varieties. Mosquito fish are another hardy option that helps control pests while being adaptable to various conditions.
Native species often prove more resilient than exotic ones, as they’ve already adapted to your local climate patterns. Consider incorporating local marsh plants around your pond’s edges – they’re typically well-suited to both wet and dry conditions.
Remember to create different depth zones in your pond to give plants and fish options for finding their preferred temperatures. Deep areas provide cool refuges during heat waves, while shallow shelves support marginal plants that help shade and cool the water.
Start with a few reliable species and observe how they perform through seasonal changes before adding more varieties. This step-by-step approach helps you build a resilient ecosystem that can weather climate challenges.
As we’ve explored throughout this article, climate change poses real challenges for our pond ecosystems, but there’s plenty we can do to protect these precious water features. By staying alert to changes in water levels, monitoring temperature fluctuations, and watching for signs of stress in our aquatic plants and fish, we can take early action to maintain healthy pond environments.
Remember, small steps make a big difference. Adding shade plants, maintaining proper water depth, and installing aeration systems are practical solutions that help our ponds adapt to changing conditions. Regular water testing and seasonal maintenance become even more crucial as weather patterns become less predictable.
Don’t wait for problems to develop – start implementing these protective measures today. Your pond is a living ecosystem that depends on your care and attention. By taking proactive steps now, you’ll help ensure your water garden remains a thriving haven for wildlife and a source of joy for years to come. Together, we can create resilient pond environments that withstand the challenges of our changing climate while continuing to enhance our outdoor spaces.
